Prompt Chaining with Foundational models
In the rapidly evolving world of artificial intelligence and natural language processing, one of the most innovative concepts emerging is Prompt Chaining. This method optimizes the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by enabling a structured, step-by-step collaboration among multiple prompts. Let’s delve into what prompt chaining is all about, its use cases, and a practical implementation.
What is Prompt Chaining?
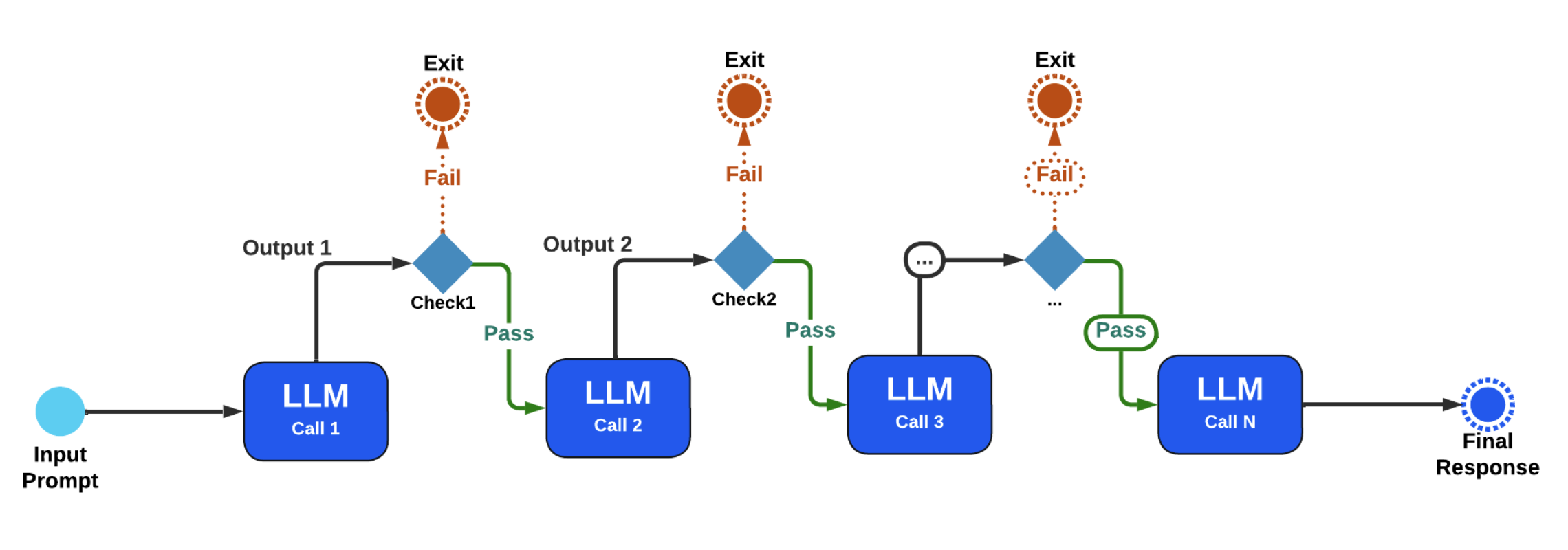
Prompt chaining is a sequential workflow where the output of one LLM call becomes the input for the next call. This allows for a more structured approach to reasoning and task completion. By chaining prompts, users can harness multiple LLM responses to achieve comprehensive, context-aware outputs.
Use Cases
The versatility of prompt chaining lends itself to a variety of applications in real-world scenarios:
- Marketing Automation: Generate marketing copy through one LLM and seamlessly translate it into different languages using another LLM.
- Document Creation: Write an outline, validate it against certain criteria, and then produce the full document based on the approved outline.
- Data Processing: Clean and standardize raw data using one LLM, then pass the refined data to another LLM for insights or visualizations.
- Question Generation and Answering: Create a list of insightful questions on a topic using one LLM, and then feed those questions into another for detailed, researched answers.
Implementing Prompt Chaining
Here’s a simplified Python example that showcases how prompt chaining works in practice:
from typing import List
from helpers import run_llm
def serial_chain_workflow(input_query: str, prompt_chain: List[str]) -> List[str]:
"""Run a serial chain of LLM calls to address the `input_query`
using a list of prompts specified in `prompt_chain`.
"""
response_chain = []
response = input_query
for i, prompt in enumerate(prompt_chain):
print(f"Step {i + 1}")
response = run_llm(f"{prompt}\nInput:\n{response}", model='meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-Turbo')
response_chain.append(response)
print(f"{response}\n")
return response_chain
# Example
question = "Sally earns $12 an hour for babysitting. Yesterday, she just did 50 minutes of babysitting. How much did she earn?"
prompt_chain = [
"""Given the math problem, ONLY extract any relevant numerical information and how it can be used.""",
"""Given the numerical information extracted, ONLY express the steps you would take to solve the problem.""",
"""Given the steps, express the final answer to the problem."""
]
responses = serial_chain_workflow(question, prompt_chain)
final_answer = responses[-1]
In this example, the function serial_chain_workflow runs three prompts that guide the LLM through the process of solving a simple math problem. Each step logically follows the previous one, which exemplifies the concept of chaining.
Beyond Prompt Chaining: Advanced Workflows
Alongside prompt chaining, other advanced workflows enhance LLM capabilities:
- Routing Workflow: Dynamically routes inputs to the most suitable LLM configuration for optimized performance.
- Parallelization Workflow: Simultaneously distributes tasks across multiple LLM calls to manage complex operations.
- Orchestrator-Worker Model: Coordinates a central orchestrator with various worker LLMs, integrating their outputs into cohesive results.
- Evaluator-Optimizer Loop: Iterates on LLM-generated outputs for continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Prompt chaining offers a powerful approach to enhancing the functionality of LLMs, allowing for more structured and logical workflows. As these methodologies continue to evolve, they will undoubtedly play a critical role in the effective application of AI in various fields, from marketing to data analysis.
For more hands-on examples and advanced techniques, check out the accompanying deep-dive notebook linked at the end of this article.
Explore the future of AI with prompt chaining and harness the next level of language processing capabilities!